How your mind works

How your mind works
The mind and worried system
The mind contains billions of nerve cells organized in patterns that coordinate idea, emotion, behavior, poke and sensation.
An superior dual carriageway system of nerves connects the mind to the relaxation of your body, so verbal change can occur in seconds. Mediate about how like a flash you pull your hand aid from a hot range. Whereas the total formula of the mind work together, every section is accountable for a particular feature — controlling everything from your coronary heart rate to your mood.

Cerebrum
The cerebrum is the very top section of the mind. Or now now not it’s what you presumably visualize in case you suspect of brains in standard. The outermost layer of the cerebrum is the cerebral cortex, also called the “gray subject” of the mind. Deep folds and wrinkles in the mind magnify the bottom house of the grey subject, so extra recordsdata might per chance well also be processed.
The cerebrum is split by a deep groove, also called a fissure. The groove divides the mind into two halves is called hemispheres. The hemispheres communicate with every other thru a thick tract of nerves called the corpus callosum on the inferior of the groove. Surely, messages to and from one facet of the body are most regularly handled by the reverse facet of the mind.

Lobes of the mind
The mind’s hemispheres have four lobes.
- The frontal lobes attend defend watch over pondering, planning, organizing, venture-fixing, short-duration of time memory and poke.
- The parietal lobes attend interpret feeling, is called sensory recordsdata. The lobes process type, texture and temperature.
- The occipital lobes process photography from your eyes and join them to the photography saved on your memory. This helps you to behold photography.
- The temporal lobes attend process recordsdata from your senses of scent, type and sound. They also play a feature in memory storage.

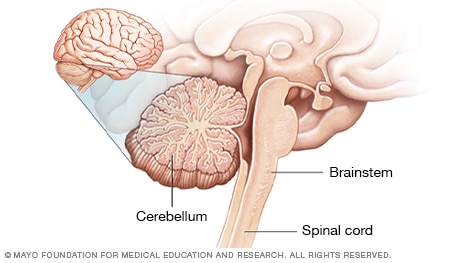
Cerebellum and brainstem
The cerebellum is a wrinkled ball of tissue below and in the aid of the relaxation of the mind. It in actuality works to combine sensory recordsdata from the eyes, ears and muscular tissues to attend coordinate poke. The cerebellum activates in case you learn to play the piano, shall we embrace.
The brainstem links the mind to the spinal wire. It controls capabilities very valuable to life, akin to coronary heart rate, blood rigidity and respiratory. The brainstem is also extreme for sleep.
The inside mind
Structures deep within the mind defend watch over emotions and memories. Identified as the limbic system, these buildings advance in pairs. Every section of this kind is most as much as the moment in every halves of the mind.
- The thalamus acts as a gatekeeper for messages passed between the spinal wire and the cerebrum.
- The hypothalamus controls emotions. It also regulates your body’s temperature and controls capabilities akin to eating or snoozing.
- The hippocampus sends memories to be saved in areas of the cerebrum. It then remembers the memories later.

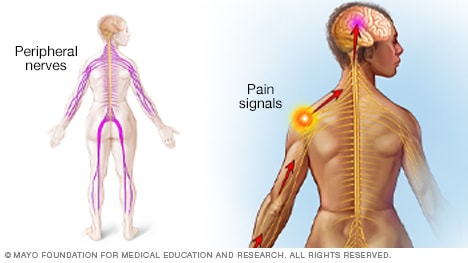
Peripheral worried system
The total nerves on your body which might per chance be outside of the mind and spinal wire originate up the peripheral worried system.
It relays recordsdata between your mind and your extremities, akin to your arms, arms, legs or feet. As an illustration, in case you contact a hot range, worry signals scuttle from your finger to your mind in a split 2d. Your mind tells the muscular tissues on your arm and hand to swiftly take grasp of your finger off the hot range.
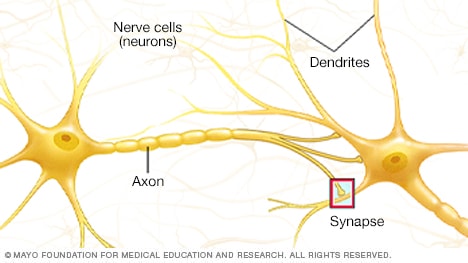
Nerve cells
Nerve cells, is called neurons, send and gain nerve signals. They’ve two foremost forms of branches coming off their cell bodies. Dendrites gain messages from other nerve cells. Axons raise outgoing messages from the cell body to other cells — akin to a close by neuron or muscle cell.
Interconnected with every other, neurons provide environment friendly, lightning-like a flash verbal change.
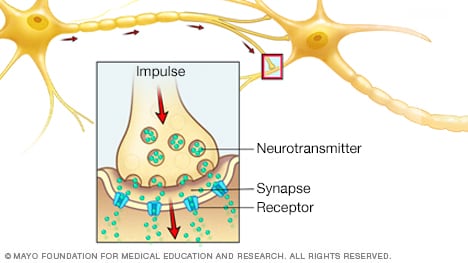
Neurotransmitters
A nerve cell communicates with other cells thru electrical impulses when the nerve cell is stimulated. Interior a neuron, the impulse strikes to the tip of an axon and causes the free up of chemical substances, called neurotransmitters, that act as messengers.
Neurotransmitters fling thru the gap between two nerve cells, is called the synapse. They then build to receptors on the receiving cell. This process repeats from neuron to neuron as the impulse travels to its fling back and forth set up. This web of verbal change that helps you to pass, think, feel and communicate.
July 02, 2024
- Mind fundamentals: Know your mind. National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. https://www.ninds.nih.gov/correctly being-recordsdata/public-training/mind-fundamentals/mind-fundamentals-know-your-mind#. Accessed Jan. 10, 2024.
- Anatomy of the mind. American Association of Neurological Surgeons. https://www.aans.org/en/Patients/Neurosurgical-Situations-and-Therapies/Anatomy-of-the-Mind. Accessed Jan. 10, 2024.
- Mind anatomy and capabilities. National Most cancers Institute. https://www.most cancers.gov/uncommon-mind-spine-tumor/tumors/anatomy/mind-anatomy-capabilities. Accessed Jan. 10, 2024.
- Overview of peripheral worried system considerations. Merck Handbook Professional Version. https://www.merckmanuals.com/authentic/neurologic-considerations/peripheral-worried-system-and-motor-unit-considerations/overview-of-peripheral-worried-system-considerations. Accessed Jan. 10, 2024.
- Ciurleo R, et al. Parosmia and neurological considerations: A passed over association. Frontiers in Neurology. 2020; doi:10.3389/fneur.2020.543275.