18 brain study that blew our minds in 2023
Possibly doubtlessly the most mysterious organ in the physique, the brain continues to astound scientists no topic the hundreds of hours they’ve spent making an strive to decipher its interior workings. Every unusual discovery in regards to the brain brings a thousand unusual questions in its wake.
Right here are 18 issues we learned in regards to the brain in 2023 that blew our minds.
Connected: Attain we the truth is use handiest 10% of our brains?
1. Newly found fragment of the brain
In January, scientists described their discovery of a extra or much less protect in the brain that helps constructive away waste and acts as a discover about-out submit for immune cells. The skinny protect appears to be to reduction preserve watch over the drift of proteins and molecules between hundreds of compartments containing cerebrospinal fluid, a colorless liquid that flows across the brain and internal tubes thru the organ.
2. Squid and human brains tied by evolution
Despite the five hundred million years of evolution that separate squids and humans, our brains make in a very identical capability to the brains of these cephalopods. Scientists found this by monitoring stem cells called neural progenitor cells in setting up squid embryos. To contain a squid retina, where diverse the animal’s neural tissue is found, the cells must first contain a prolonged, densely packed tell that can additionally be spotted all thru the neural tell of vertebrates admire us.
3. ‘Junk DNA’ and worthy brains
The genes that enabled humans to develop particularly worthy brains may maybe have initially build approach from “junk DNA,” which doesn’t code for any proteins, researchers revealed early this year. At some level in human evolution, after we split from hundreds of primates, some of this junk DNA picked up the flexibility to encode proteins. In animal and lab-dish experiments, plenty of of these genes regarded key for reinforcing brain tell.
4. Injuries plugged with minibrains
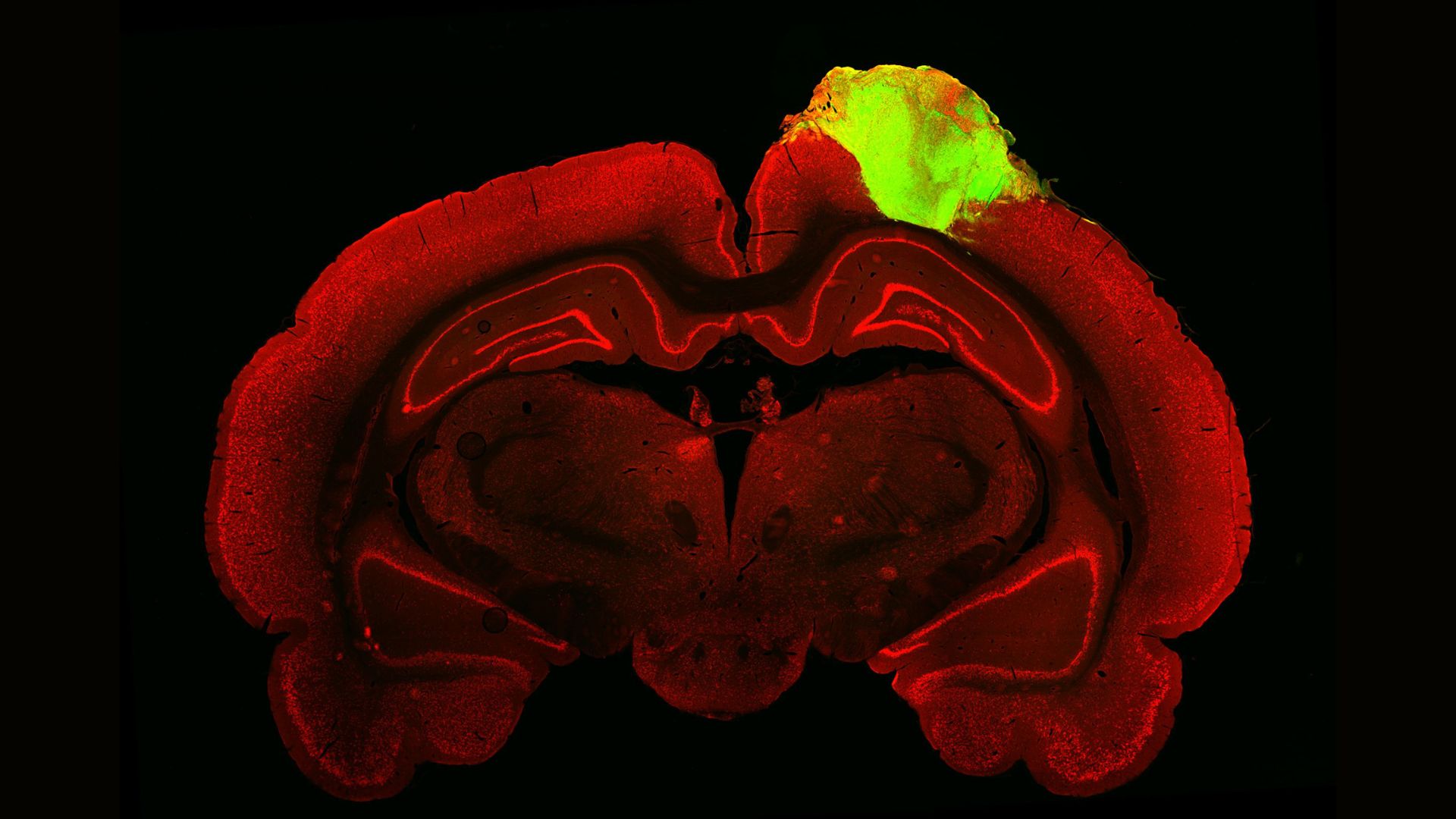
Scientists dilapidated cerebral organoids — little 3D objects of the brain — to repair brain injuries in rats. The organoids had been grown from human stem cells and transplanted into rats’ visible cortices, the build of the brain where records from the eyes is initially build processed. The researchers hope to finally note the draw in humans, nonetheless that is many years away.
5. Native language wires the brain
An individual’s native language may maybe impression how their brain hyperlinks up records-processing hubs internal its tell, per a gaze of of us whose native languages had been German and Arabic revealed in February. Variations in the gaze participants’ brains had been chalked as a lot as linguistic variations between the languages. Nonetheless, extra work is desired to characterize how cultural functions of conversation may maybe form brain tell.
6. Psychedelics invade brain cells
Psychedelics have confirmed promise as therapies for exhausting-to-take care of despair, and now scientists deem it can be because they invade brain cells. Psychedelics, comparable to LSD, DMT and psilocybin, can bind to receptors for the chemical messenger serotonin — nonetheless drastically, they’ll latch onto these receptors on the out of doors and internal of cells. Theoretically, this capability psychedelics may maybe flip switches that gentle antidepressants, which on the total lengthen the focus of serotonin out of doors the cells, cannot reach. That would be why trippy remedy power brain cells toward constructing unusual connections.
7. Beneath no circumstances-sooner than-viewed brain wave
Octopuses generate one of those brain wave no longer viewed in any hundreds of animal, even humans. These prolonged-lasting, surprisingly slack brain waves had been recorded the usage of electrodes implanted in freely transferring octopuses’ brains. Scientists are no longer but definite what feature these distinctive waves wait on, or if they’re tied to a particular behavior.
8. Rapid-circuiting persistent ache
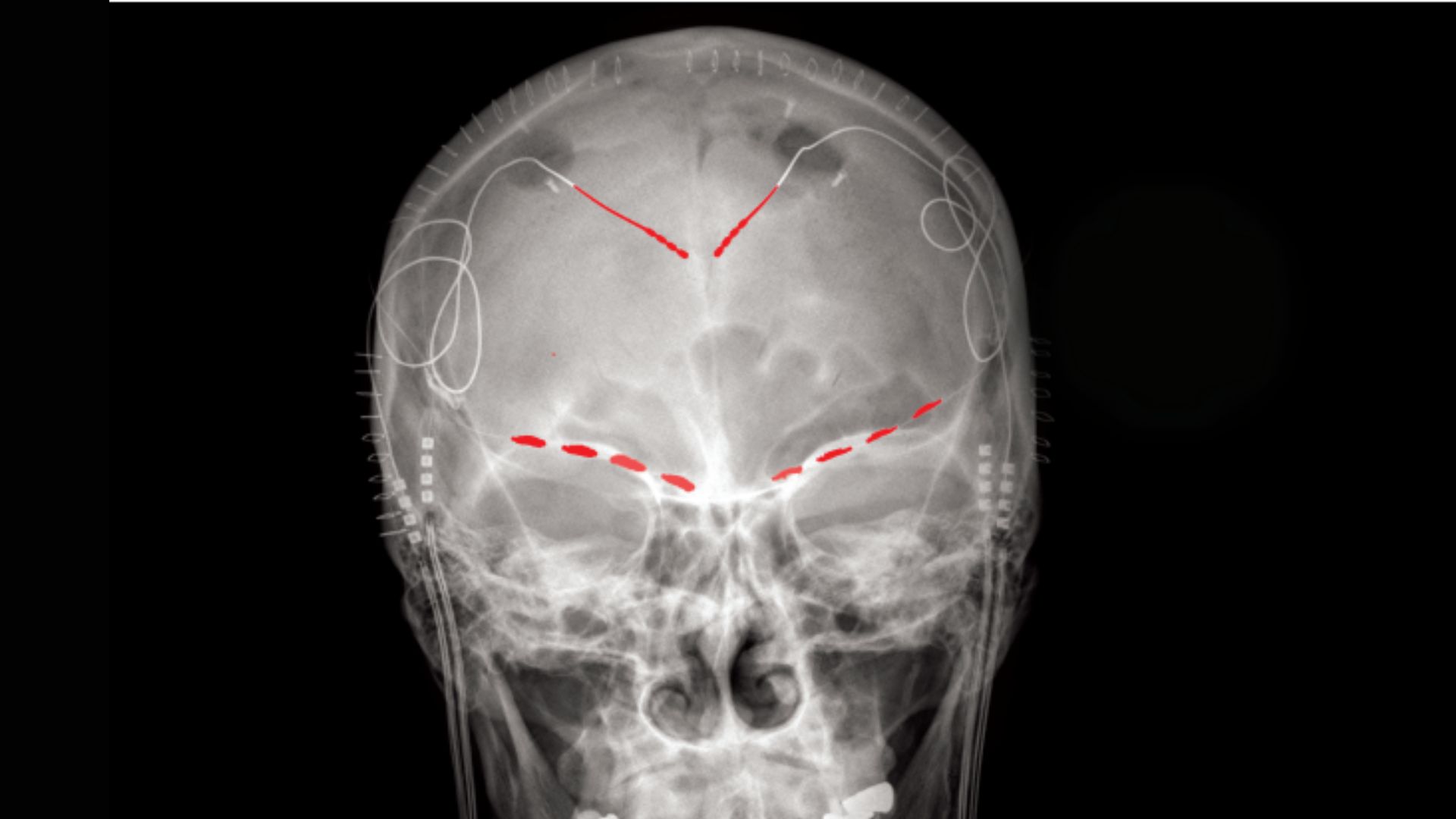
The brains of of us with persistent ache cowl fluctuating patterns of activity that will doubtless be tied to the subjective expertise of their ache, researchers have found. Decoding these patterns may maybe sooner or later enable doctors to disrupt them with focused therapies, thus quick-circuiting sufferers’ ache.
9. Brain surgical treatment in the womb
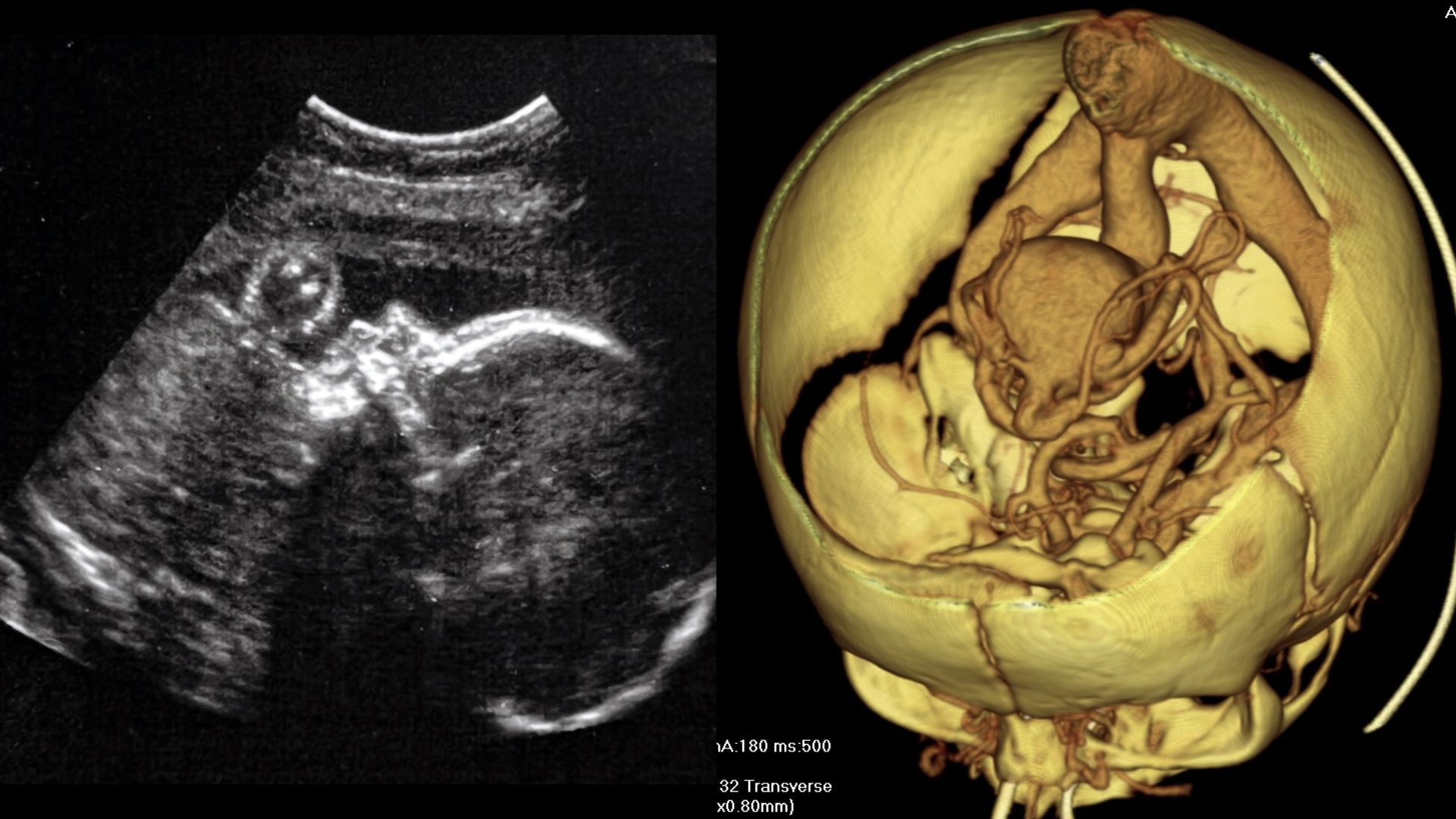
In a first-rate-of-its-variety surgical treatment, doctors repaired a malformed blood vessel in a fetus’ brain sooner than birth. The malformation happens in an estimated 1 in 60,000 births and is on the total handled after birth, when it can have to veritably be too silly to pause hurt or loss of life. In March, doctors successfully handled the malformation sooner, in the womb.
10. Life flashing sooner than your eyes?
Of us’s brains generate a flurry of activity of their final minutes of existence, scientists revealed in Could honest, and this electrical surge may maybe judge unsleeping experiences — nonetheless, that is upright a thought. It can maybe be that this activity erupts as of us “transfer toward the sunshine” or gaze their “lives flashing sooner than their eyes,” as portrayed in many movies. Or, it can also upright be “aberrant electrophysiological activity,” some consultants enlighten.
11. Thriller brain spiral indicators
Spiral indicators uncovered in the human brain may maybe reduction position up the organ’s complex activity. The spirals are brain waves that circulate over the outside of the brain and rotate spherical central points. These spirals may maybe act as bridges of verbal replace between hundreds of areas of the brain, scientists theorized in June.
12. Sex swap in mouse brains
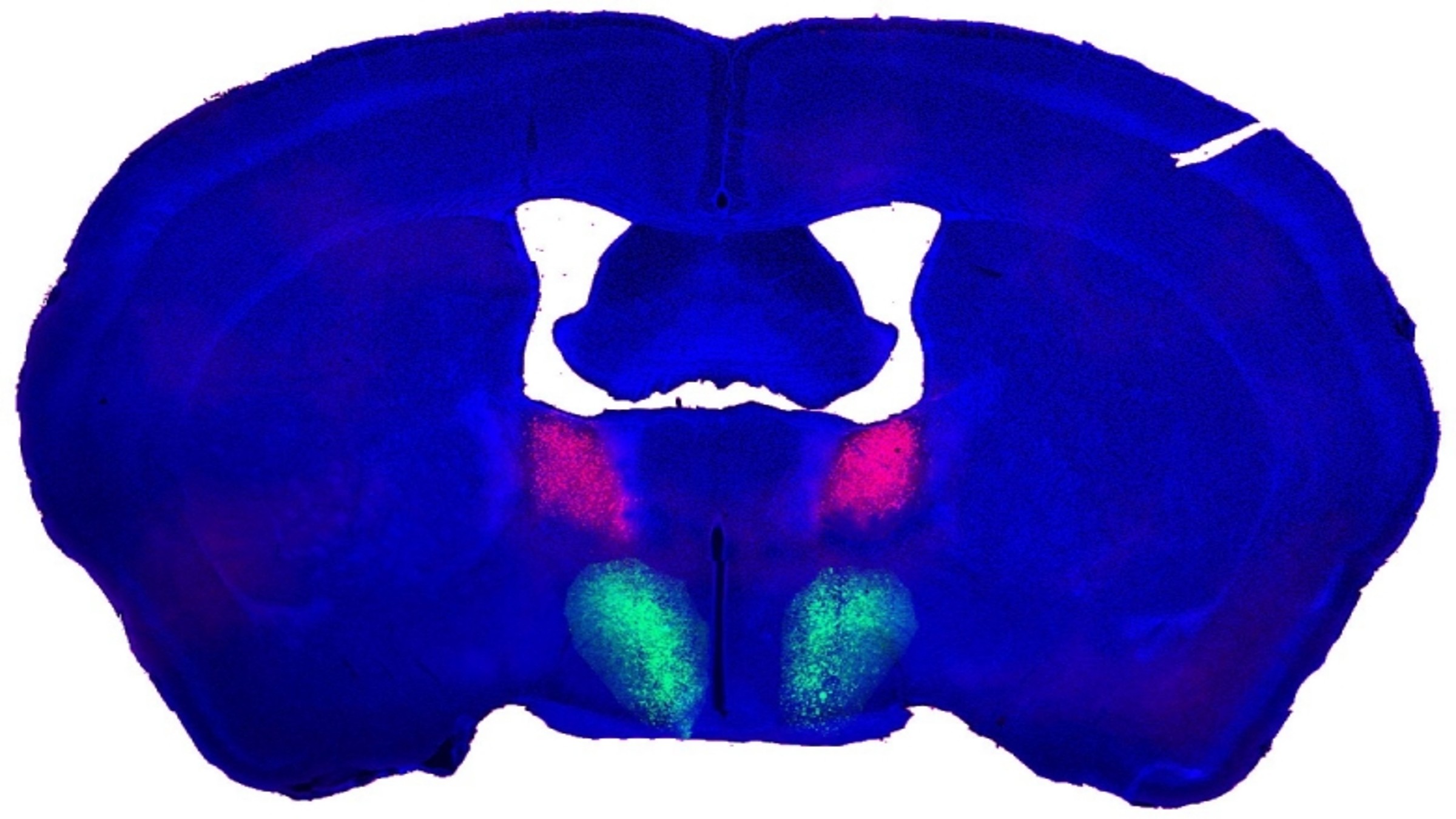
Scientists found an “on swap” for libido in the male mouse brain — and they deem a identical preserve watch over center may maybe exist in humans, although they haven’t found such circuitry but. Flipping the swap drove male mice to mate with females and with inanimate objects, and additionally diminished the damage time wanted between rounds of intercourse. As of now, no identical circuit has been cowl in female mice.
13. Pink Floyd in brain waves
In August, scientists revealed they had been ready to “read” of us’s brain waves and recreate Pink Floyd’s neatly-known “One other Brick in the Wall,” which the volunteers had listened to all thru their brain recordings. Some song snippets generated by the researchers the truth is did sound admire the 1979 sing song — hundreds of snippets, nonetheless, sounded a lot muddier.
14. A ‘characterize’ for unsuitable memories
Your brain’s activity shifts in an very excellent capability when you are about to recall a unsuitable memoryor one wherein the events never the truth is took build. This “characterize” particularly vegetation up in the hippocampus, a key brain build for memory, scientists right this moment found.
15. Brain changes across menstrual cycle
The brain’s tell goes thru subtle changes all over a person’s menstrual cycle. These changes appear in the microstructure of the brain’s white topic — the insulated wires that trail between brain cells — besides the thickness of its gray topic, the our bodies of brain cells. For now, it be unknown whether or no longer these brain changes affect cognition or the possibility of brain ailments. Nonetheless the study may maybe commence the door to such discoveries in due direction.
16. Complete insect brain scheme
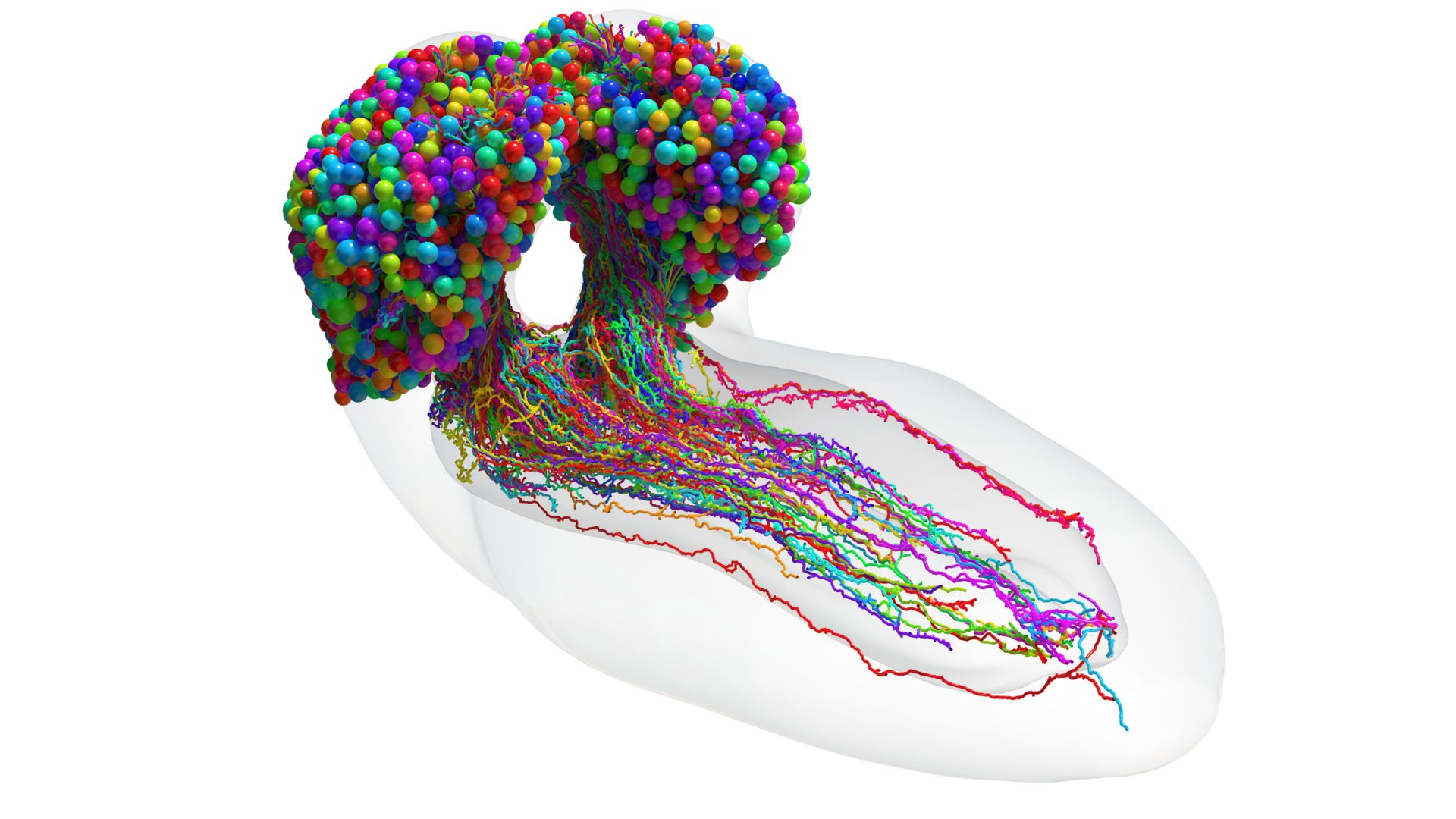
The first-ever total scheme of an insect’s brain incorporates 3,016 neurons. The fruit cruise brain atlas, finished over 12 years and finally revealed in June, exhibits your total bodily connections between the thousands of cells. It can maybe reduction pave the capability for added-developed man made intelligence (AI) systems and reduction scientists decipher identical structures in the human brain.
17. Most-total human brain scheme ever
This year, scientists unveiled the most detailed atlas of the human brain ever conceived which well-known points the affiliation of 3,300 forms of brain cells, few of which had been previously known to science. The atlas is half of quiet of neurons — the brain cells that talk thru chemical and electrical messages — and half of made up of non-neuronal cells.
18. Minibrain plugged into AI
For the first time, scientists plugged a brain organoid into the heart of an AI system and dilapidated the hybrid computer to fabricate tasks and computations. The experiment may maybe reduction pave the capability for biocomputers that borrow strategies from biology to become extra vitality environment friendly than same old computers.
Ever wonder why some of us contain muscle extra without complications than others or why freckles approach out in the sun? Ship us your questions about how the human physique works to neighborhood@livescience.com with the topic line “Neatly being Desk Q,” and likewise you may gaze your query answered on the web sta ever!