Why Is the Ocean Salty?
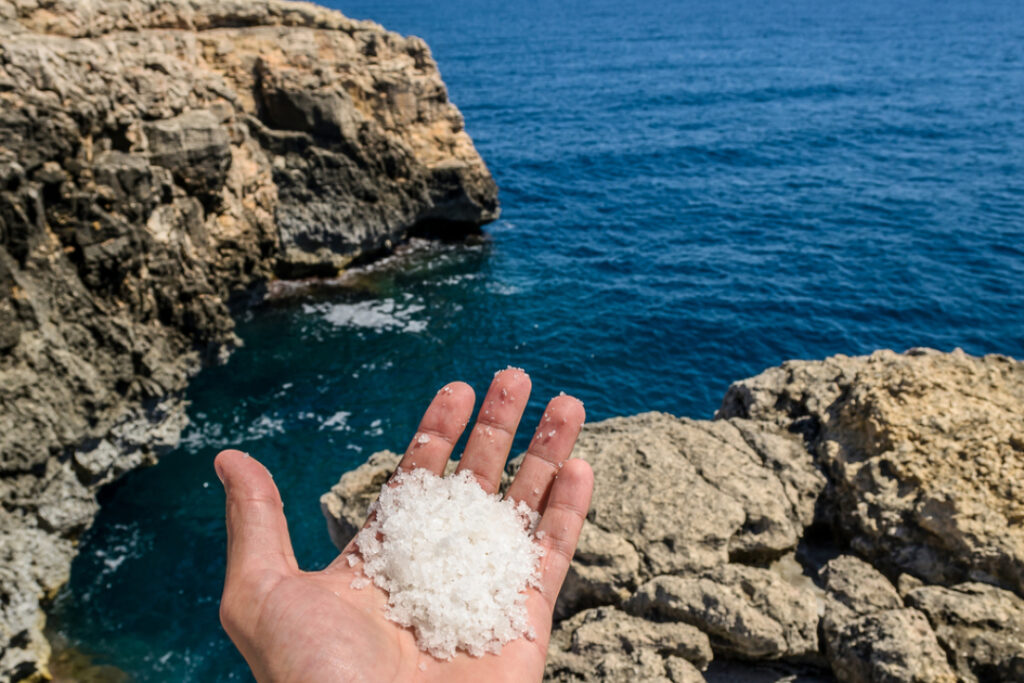

If you’ve ever had the anxiety to swallow a mouthful of seawater, you have some thought of its intense salinity. One miniature gulp is spoiled sufficient, however the general salt philosophize of Earth’s oceans is in actuality staggering: In step with a median of 7 tablespoons per liter, scientists have calculated that they address about 50 quadrillion loads (that’s 15 zeros) of dissolved salt.
Extra inconceivable peaceable, it wasn’t frequently there. It trickled slowly into the ocean — grain by grain, year by year — from the mountains, hills and plains of the terrestrial panorama. To look at why, we first must always understand about a issues about salt.
Where Salt within the Ocean Comes From
Salt is a lot larger than a dinner-table seasoning. In chemistry, the term refers to any compound with positively and negatively charged ions — no longer real the sodium chloride we utilize to present a enhance to our cooking, but also magnesium, sulfate, potassium and hundreds others.
These diverse salts are most up-to-date in rocks all around the arena. And as pure forces fancy freezing and thawing break rocks down into smaller and smaller chunks, their minerals (salt included) are flushed against the ocean by erosion.
All alongside the formulation, on fable of of their ions, salts are also at possibility of a 2nd negative task: chemical weathering. The hydrogen atom in every water molecule has a detrimental rate, and the oxygen atom has a distinct rate. Because opposites attract, rain and rivers are ready to surround and dissolve salt ions as they wash over the panorama.
For that topic, you glean the same win in underground volcanoes. “It’s taking place wherever that water gets eager with rocks,” says Colin Stedmona chemical oceanographer on the Technical University of Denmark. “Water is the closing solvent.”
Read Extra: Salt Played a Pivotal Characteristic in Historical Human History
Why Don’t Lakes and Rivers Maintain As Mighty Salt?
Every fall of that salty resolution at closing winds up within the ocean. But it all comes from rivers, and one plot or the other they seem unaffected by their brackish cargo.
It appears there is somewhat of salt in every supposedly “recent” body of water. It’s no longer sufficient to your tastebuds to detect, but when these hint amounts attain their closing vacation plight, they combine to pack a seriously briny punch.
That’s on fable of once salt is deposited within the ocean, it gets great extra concentrated as water evaporates into the ambiance — a new generation of rain quickly heads off to erode the subsequent batch of minerals, whereas salt crystals win left on the reduction of.
Read Extra: Why Are People So Drawn to Water?
Sea Salt
They don’t cease there with no break in sight, even supposing. Over time, an expansion of pure processes get rid of salt from the oceanic system. In shallow coastal waters, the focus can win so excessive that no extra can also moreover be dissolved, and a few then precipitates to make a layer on the bottom. That’s where we win our loved sea salt, with its distinct, complex style.
Ocean water also seeps into deep-sea fissures, dragging salt down into the interior mantle, where it will also once extra glean its formulation into rocks that will someday resurface on the continents. When that occurs, the cycle restarts anew.
Silent, there’s a considerable mismatch between water and salt cycles (basically based on Stedmon, the latter is hundreds of times slower). Water is in constant flux, whereas salt takes eons to switch from assign to assign. In consequence, the ocean has turn out to be extremely saline, whereas our inland water sources remain drinkable.
In spite of their vastly assorted timelines, then again, the cycles have reached equilibrium. The ocean may perchance well dissolve far extra salt than it currently consists of, but it indubitably isn’t getting any saltier. On the opposite hand great the rivers express, a roughly connected amount gets withdrawn. “There’s a extremely unhurried present,” Stedmon says, “balanced with a extremely unhurried removal.”
Read Extra: Companies, Conservationists Battle for the Deep Sea
Why the Ocean’s Salt Remark material is Vital
Salt may perchance well be indubitably one of basically the most misplaced sight of gamers on the arena stage. It doesn’t real drift around without honest; in truth, it’s responsible for a lot of Earth’s climate.
Ocean currents, which circulate into warmth and chilly water around the planet, are wanted regulators of the world native climate. And these currents, in flip, are created basically by wind, water temperature, and — you guessed it — salinity.
Splendid as meteorologists measure air temperature to foretell what’s going to happen within the ambiance, oceanographers measure these elements to mannequin the prolonged trip activity of currents (which, as already renowned, also influences atmospheric climate).
The oceans are in actuality dotted with independent robotic sensors from the world ARGO program. They mechanically sink down hundreds of ft, fancy climate balloons in reverse, to safe recordsdata. Because we know precisely how effectively saltwater conducts electricity, they pump some by means of a conductivity cell to check its salinity. Then they relay the outcomes to climate stations.
The forecasts they abet generate are wanted for all our interactions with the ocean, from transport to wave energy harvesting. Currents also transport the nutrients that retain marine existence, which formulation we can utilize them to trace fish populations.
As Stedmon puts it, “there’s an speedy hyperlink between [current] circulation and the plot in which we utilize the ocean.” And, he adds, an equally major hyperlink between circulation and salt.
Read Extra: Why It is Alarming That Deep-Sea Currents are Starting to Sluggish
Article Sources
Our writers at Discovermagazine.com utilize look for-reviewed be taught and excessive-quality sources for our articles, and our editors evaluate for scientific accuracy and editorial standards. Review the sources outmoded below for this article:
-
Sci Fetch. Atmosphere injection of sea salts at some level of mammoth explosive submarine volcanic eruptions
-
Colin Stedmon. Chemical oceanographer on the Technical University of Denmark
-
NOAA. ARGO program
-
Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments. Advances and challenges in ocean wave energy harvesting
Cody Cottier is a contributing author at Leer who loves exploring big questions relating to the universe and our dwelling planet, the nature of consciousness, the ethical implications of science and extra. He holds a bachelor’s diploma in journalism and media manufacturing from Washington Notify University.
Read More