11 jaw-shedding fossil discoveries that weren’t dinosaurs in 2023

Dinosaurs repeatedly snatch the limelight by methodology of fossils, but utterly different prehistoric critters are correct as deserving of our attention. As 2023 comes to a stop, or now not it’s a long way time to observe back on some of basically the most jaw-shedding fossil discoveries that weren’t all about T. rex. From a fish with eyes too gargantuan for its belly to the excellent ever fossilized flower and mysterious marine fossils that glow gold, here is our pick of non-dino fossils that blew our socks off in 2023.
Most attention-grabbing penguin to stroll Earth
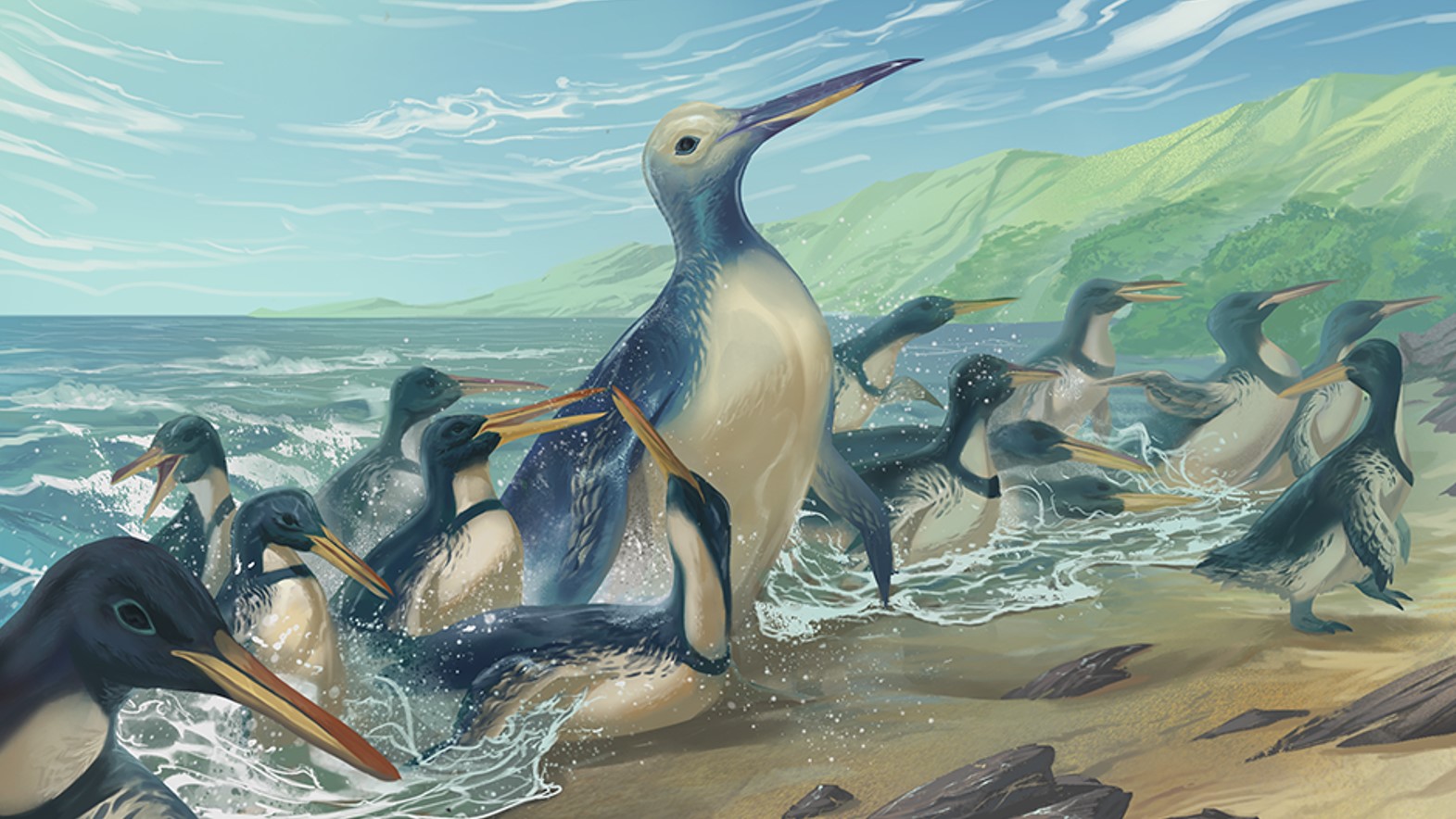

In February, scientists described fossils belonging to the excellent identified species of penguins — Kumimanu fordyceiwhich weighed a whopping 340 kilos (154 kilograms). These colossal penguins glided thru the ocean around what is now Fresh Zealand bigger than 50 million years prior to now, bones found out internal coastline boulders in North Otago on the nation’s South Island printed.
Researchers estimated the burden of K. fordycei in step with the scale and density of these bones compared with those of residing penguins. The fossilized stays of eight utterly different penguin specimens had been also uncovered contained in the boulders, including those of the newfound species Petradyptes stonehousei and a identified species of big penguin, K. biceae.
Big penguins probably disappeared around 27 million years prior to now, when they had been outcompeted by marine mammals similar in dimension, experts told Dwell Science.
Tiny penguin skulls
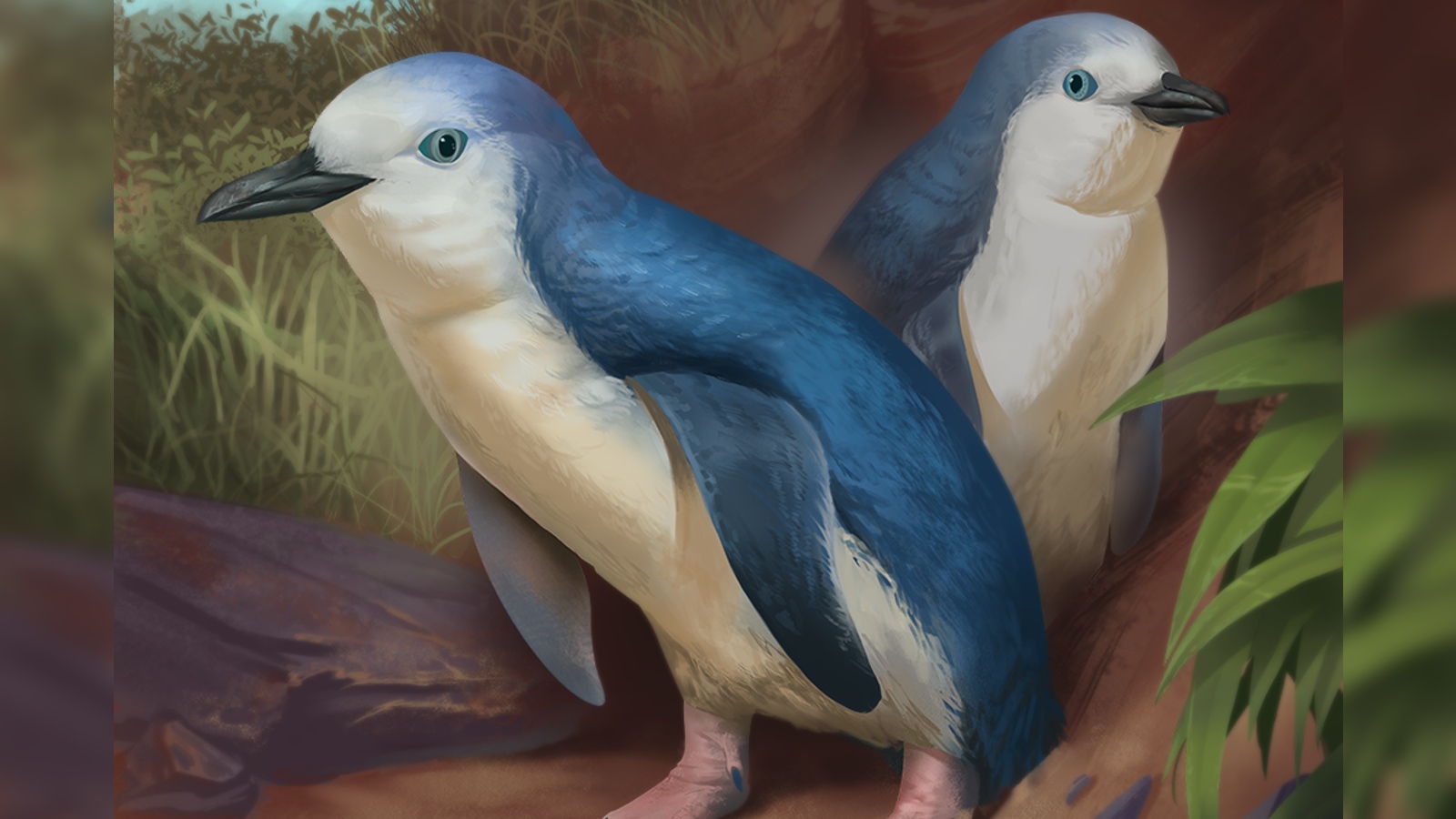

In June, researchers identified two tiny cranium fossils from Fresh Zealand’s North Island as belonging to a by no methodology-earlier than-considered extinct species, which they named Wilson’s minute penguin (Eudyptula wilsonae). The skulls, one from an adult and the utterly different from a juvenile, had been remarkably equivalent to those of the smallest residing species of penguin this day — the minute penguin (Eudyptula minor).
Researchers do now not know exactly how tiny the extinct birds had been, but minute penguins develop to a maximum dimension of 13.5 inches (35 centimeters) and weigh around 2 kilos (0.9 kg), which can be in the ballpark.
Linked: Former skeletons of excellent-ever marsupial unearthed in Australia
Fossilized flower mystery solved
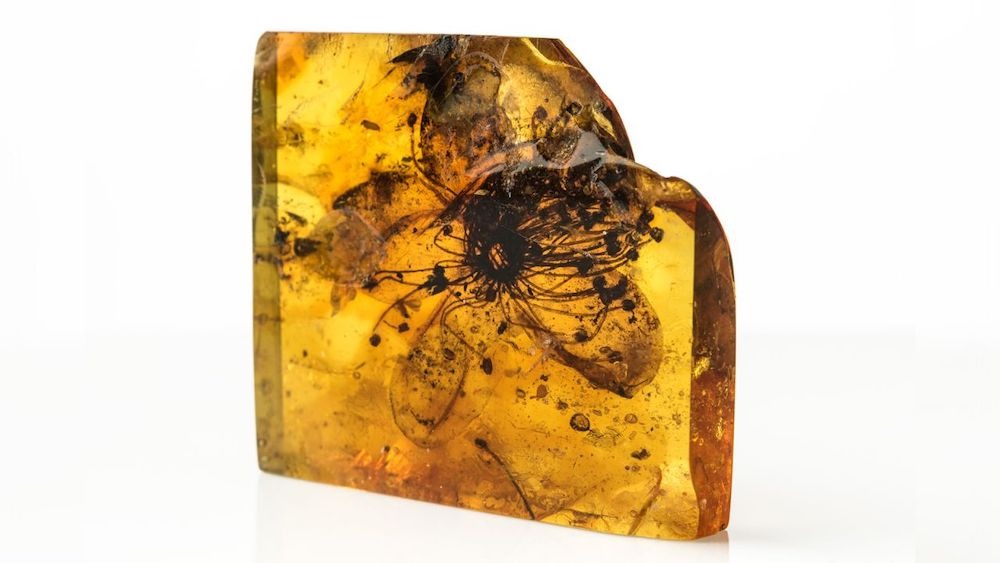

In January, scientists in the smash obtained to the backside of a 150-year-outdated college mystery. They found out that a flower entombed in a hunk of amber and located out in the Baltic forests of Northern Europe in 1872 is a newfound species named Symplocos kowalewskii that dates to the tedious Eocene epoch (roughly 38 million to 33.9 million years prior to now).
The specimen, which measures about 1 crawl (2.8 cm) wide, is the excellent fossilized flower ever recorded and is thrice the scale of the next-excellent amber-encased bloom.
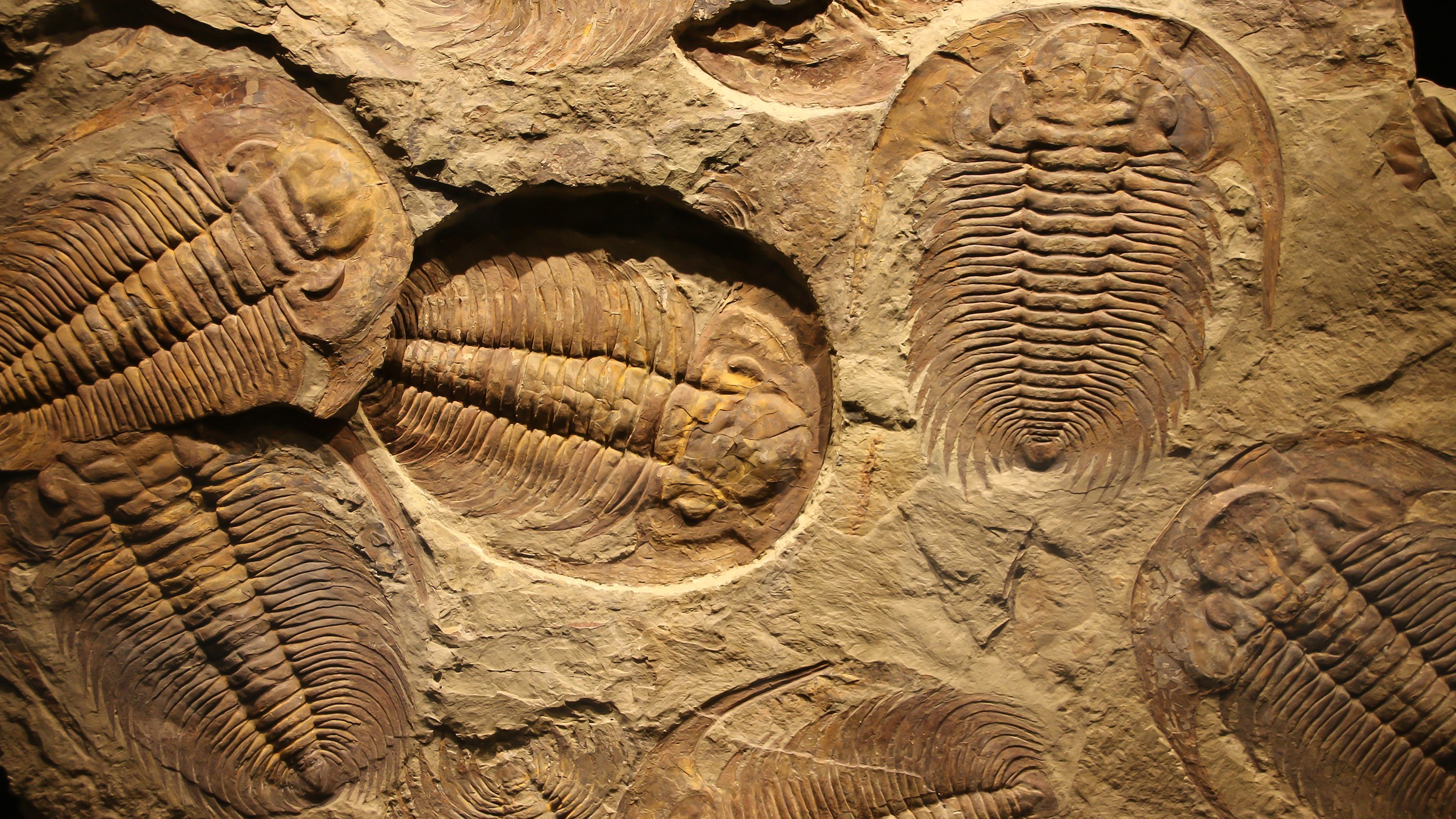

Scientists examining a fossilized trilobite specimen — an extinct marine arthropod that lived all the arrangement thru the Paleozoic Era (541 million to 252 million years prior to now) — found out that these prehistoric creatures didn’t admire correct a pair of compound eyes, as previously view, but additionally sported a third peek in the course of their forehead.
The trilobite specimen became once missing an a part of its head, which gave researchers a look beneath a layer of shell that turns into opaque all the arrangement thru the fossilization path of and obscures the constructions beneath. Hidden median eyes are total among arthropods residing this day.
Tiny one turtles unsuitable for vegetation
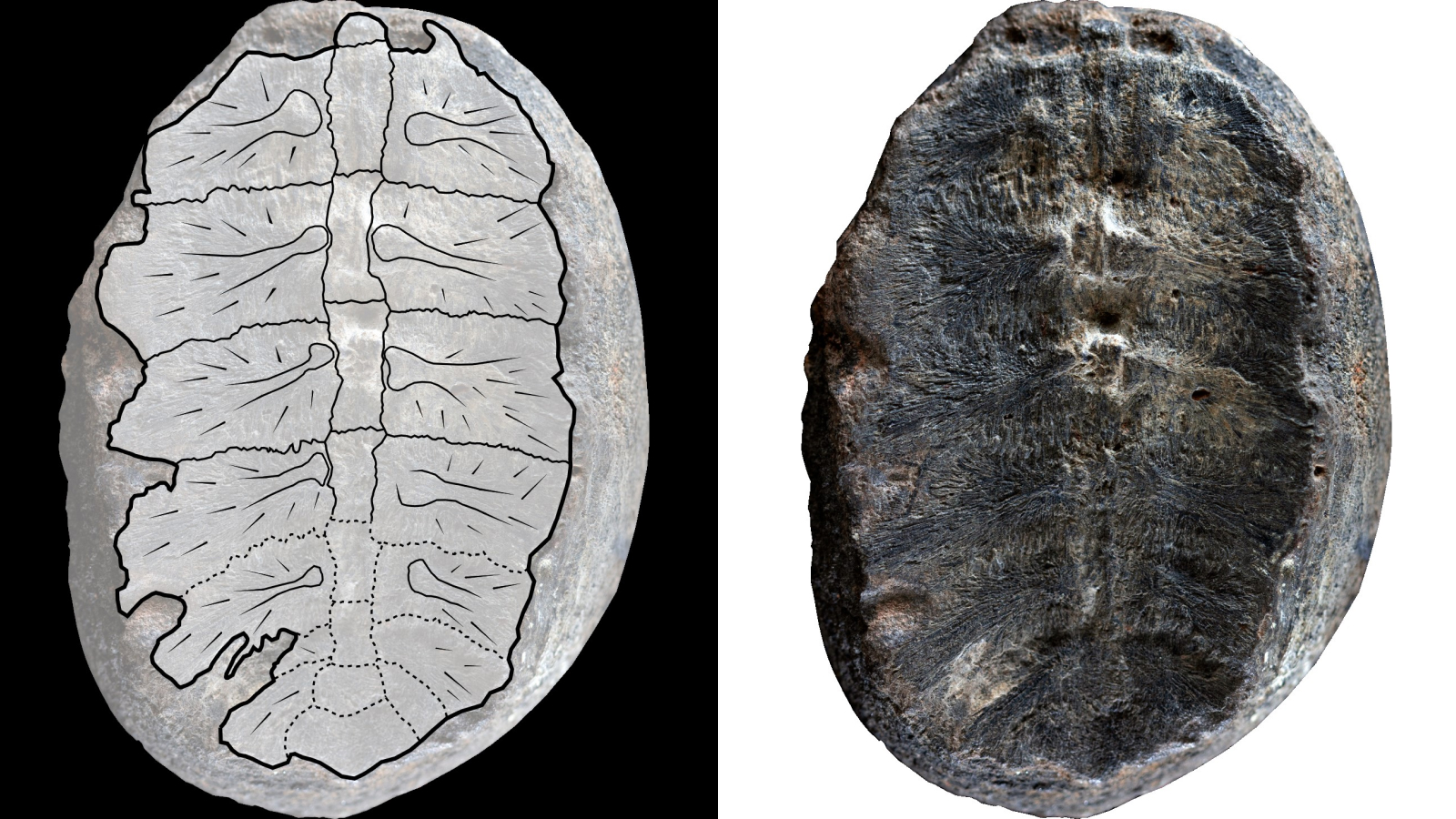
A re-examination of two dilapidated “plant” fossils found out in Colombia 50 years prior to now printed they are in fact the stays of hatchling turtles from the dinosaur age. The 2-crawl-prolonged (5 cm), leaf-shaped fossils fooled their finder, who firstly set up placed them within a group of vegetation that thrived all the arrangement thru the Slack Devonian (419.2 million to 358.9 million years prior to now) and the Permian (298.9 million to 251.9 million years prior to now).
In December, it turned out the fossils had been extremely rare imprints of the upper shells of toddler turtles relationship back to the Aptian age (125 million to 113 million years prior to now) of the Cretaceous (145 million to 66 million years prior to now).
It be conceivable the hatchlings had been individuals of the oldest sea turtles on story — Desmatochelys padillai — but researchers would desire a entire skeleton to verify this.
Linked: Flesh-ingesting ‘killer’ lampreys that lived 160 million years prior to now unearthed in China
Beheaded in action
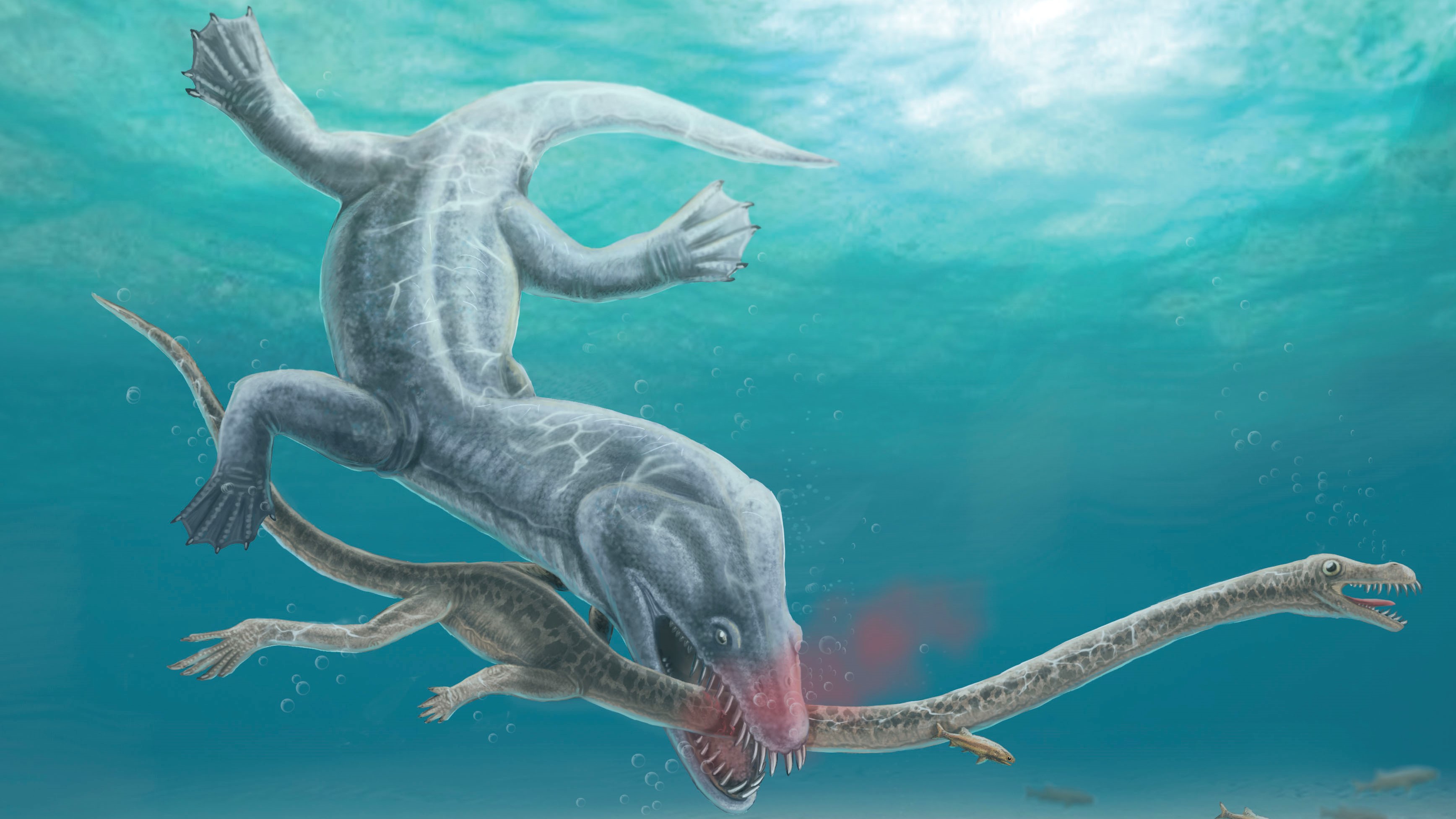

A fossil from the Center Triassic (247 million to 237 million years prior to now), which became once found out on the border between Italy and Switzerland, confirmed bone breaks and teeth marks in step with a brutal beheading. The victim, a gargantuan marine reptile called Tanystropheus hydroides with a neck thrice as prolonged as its torso, had its head torn off in a single fine chunk by an very good deadlier creature that probably swooped down from above, experts said.
It be unclear which predator could perchance perchance admire killed the 20-foot-prolonged (6 meters) reptile, but researchers narrowed down a listing of suspects by measuring the gap between the teeth marks. Potential candidates consist of the 18-foot-prolonged (5.5 m) ichthyosaur Cymbospondylus buchseri; an limitless reptile measuring as a lot as 23 ft (7 m) prolonged called Nothosaurus giganteus; and Helveticosaurus zollingeri — an enigmatic, 12-foot-prolonged (3.6 m) predator.
Slasher dolphin with jutting enamel
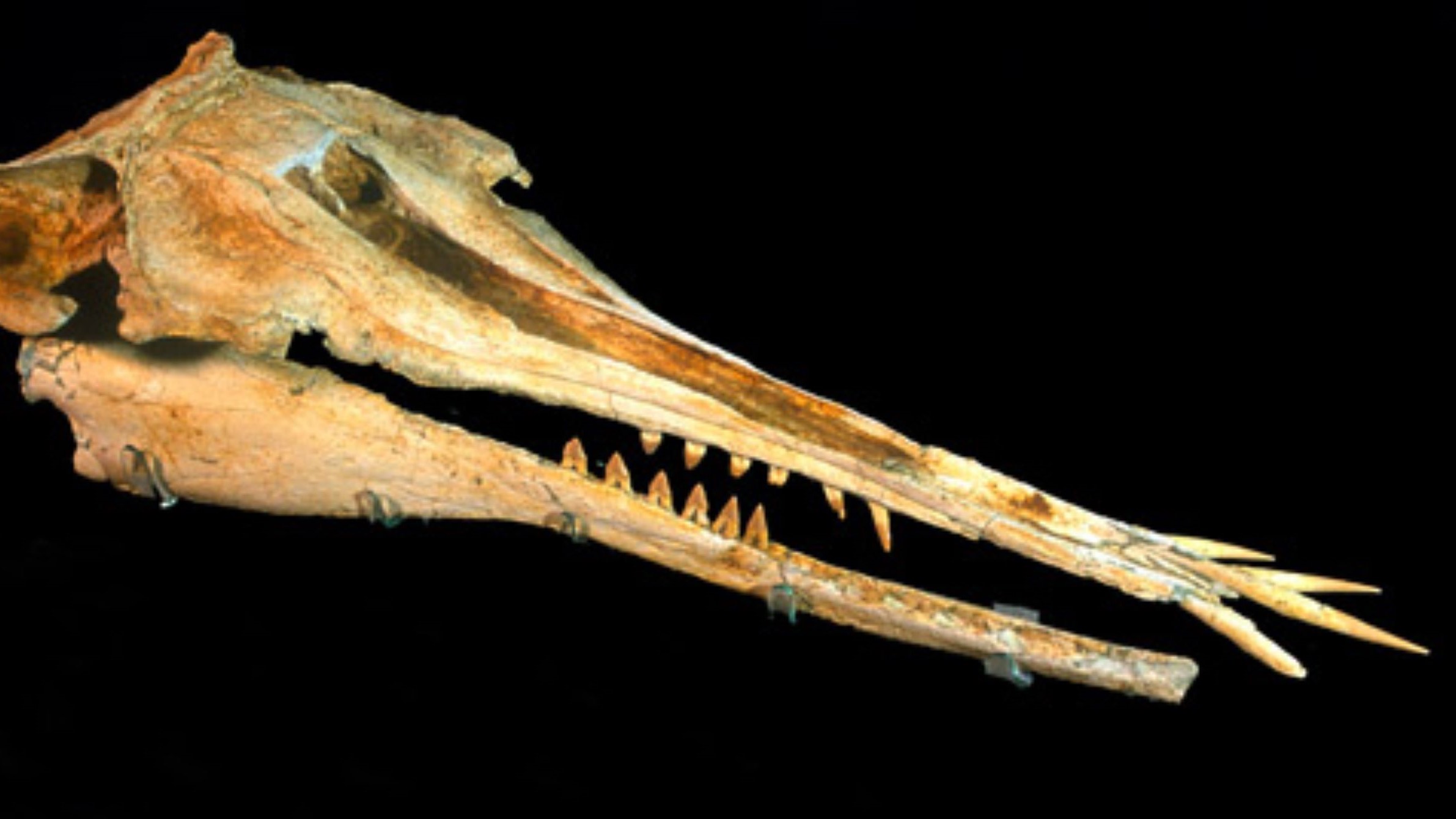

In June, researchers identified a stunningly preserved dolphin cranium as a newfound species that lived 25 million years prior to now all the arrangement thru the Oligocene duration (34 million to 23 million years prior to now). The fossil, which became once first found out buried in a cliff face in 1998 and became once being held in a museum sequence in Fresh Zealand, became once just currently named Nihohae matakoifrom Maori phrases which methodology “slashing enamel, face attractive.”
The cranium became once around 2 ft (60 cm) prolonged and sported prolonged enamel that caught out nearly horizontally from what would had been the snout. These spade-take care of enamel had been doubtlessly unsuited to catching fish, the researchers said, but the creature could perchance perchance admire thrashed at its prey to stun it earlier than slurping it up. It be also conceivable the dolphin’s jutting enamel served a sexual or social reason.
Prehistoric fish’s final supper
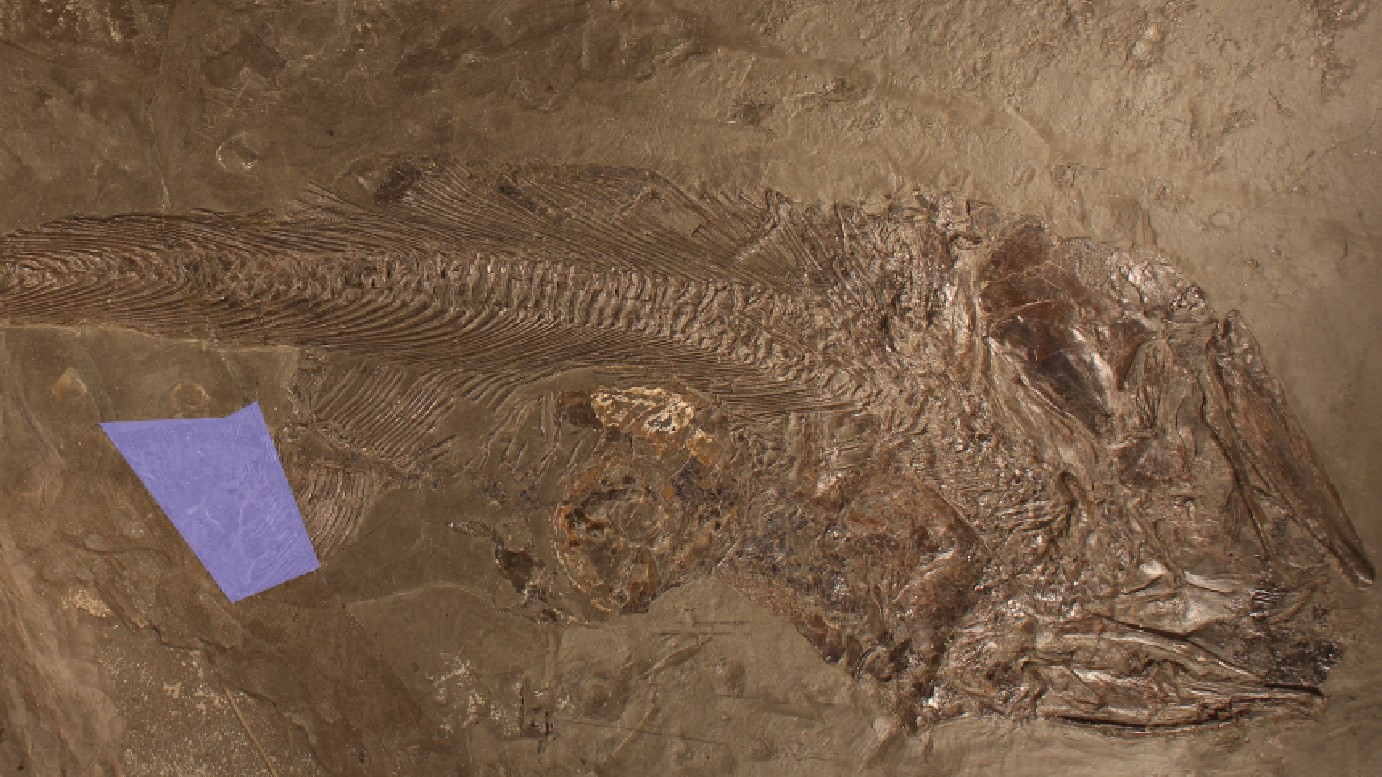

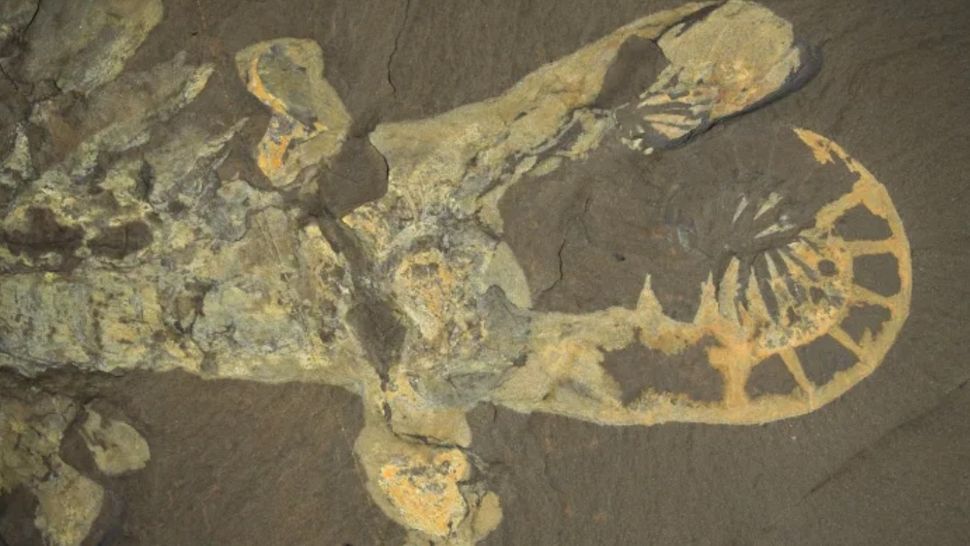
A sexy fossil found out in a museum drawer captured the second a prehistoric fish swallowed an ammonite — an extinct marine mollusk — and choked to death on it. The ammonite remained intact contained in the fish’s physique and turned into imprinted in rocks, lodged up towards the predator’s spine. The pair probably died together about 180 million years prior to now, all the arrangement thru the Jurassic duration (201 million to 145 million years prior to now).
The fossil became once found out in 1977 near Stuttgart, in southwest Germany, but researchers firstly set up saved it away, as they view the pairing of the fossilized fish and ammonite became once a coincidence. One more watch just currently printed the ammonite became once contained in the fish and sure triggered its death as a result of mollusk’s dimension — a lot like a human swallowing a dinner plate.
Mysterious golden fossils

Gleaming fossils of marine animals from Germany’s Posidonia Shale had been prolonged view to glow gold due to a mineral called pyrite, but they turned out to comprise minute or no of it. In its set up, researchers traced the fossils’ golden glimmer to phosphate minerals with yellow calcite. In incompatibility to pyrite, phosphate minerals need oxygen to smash, which printed recent records referring to the fossilization path of in the self-discipline.
Fossils from the Posidonia Shale — which consist of ammonites, bivalves and crustaceans from the Jurassic duration — are found out in what researchers once view became once a actually oxygen-depleted atmosphere. The invention of phosphate minerals in the grooves methodology a burst of oxygen will deserve to admire reached them sooner or later, turning the fossils into what looks take care of gold.
Mystery of prehistoric small’s supper solved

A small-take care of Cambrian critter’s sequence of food has bowled over scientists: It became once view to feed by piercing onerous-shelled prey, but it no doubt turns out it probably hunted gentle-bodied animals as an substitute. In July, computer units of fossils relationship to 500 million years pri or to now suggested Anomalocaris canadensiswhich became once referring to the scale of a condo cat and boasted two spiky facial appendages, doubtlessly swam take care of a cuttlefish with its appendages outstretched to pincushion prey.
Contrary to what became once previously view, A. canadensis‘ appendages doubtlessly weren’t tough ample to skewer trilobites — extinct marine arthropods with a tricky exoskeleton. So the odd creature more probably feasted on squishy animals floating in the water column.
Fleeing vampire with attractive organs

A recent prognosis of fossils belonging to a group of largely extinct, octopus-take care of creatures called vampyromorpha printed a previously undescribed species with eight hands, sucker attachments take care of a vampire squid and glow-in-the-sad organs.
The 3.2-crawl-prolonged (8 cm), bullet-shaped creature stalked Earth’s oceans 165 million years prior to now and sure snatched prey the utilization of its hands. Researchers in France named it Vampire repellent ink — a mixture of the Serbian word for vampire, “vampir,” and the Latin word for fleeing, “fugiens” — which methodology the fleeing vampire.







