Decoding cell replicational age from single-cell ATAC-seq records
- Study Briefing
- Printed:
Subject issues
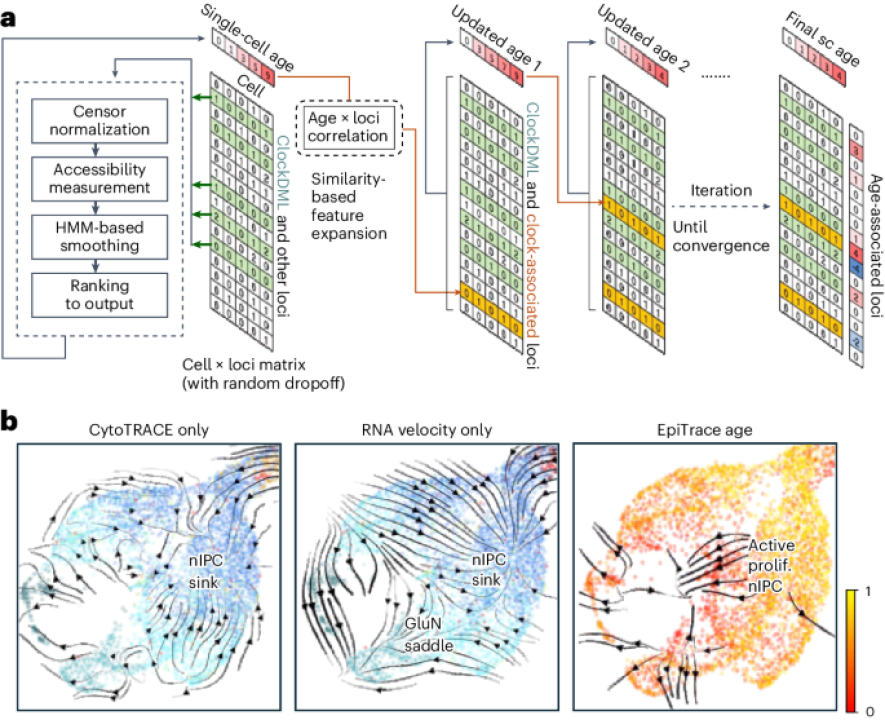
The replicational age of single cells provides a temporal reference for tracking cell destiny transition trajectories. The computational framework EpiTrace measures cell age the usage of single-cell ATAC-seq records, specifically by brooding about chromatin accessibility at clock-relish genomic loci, enabling the reconstruction of the historical past of developmental and pathological processes.
Here’s a preview of subscription snarl, glean admission to through your institution
Get entry to suggestions
Get entry to Nature and 54 assorted Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our most effective-label on-line-glean admission to subscription
$29.Ninety nine / 30 days
murder any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print elements and on-line glean admission to
$209.00 per one year
very finest $17.42 per bid
Aquire this article
- Occupy on Springer Link
- On the spot glean admission to to elephantine article PDF
Costs will likely be field to local taxes that are calculated for the length of checkout

References
-
Weng, C. et al. Deciphering cell states and genealogies of human haematopoiesis. Nature 627389–398 (2024). This paper studies that excessive-option single-cell phylogeny will be resolved by the usage of error-corrected somatic mutation profiling on the mitochondrial genome.
-
Trapp, A. et al. Profiling epigenetic age in single cells. Nat. Ageing 11189–1201 (2021). This paper studies a bioinformatic methodology to unravel cell replicational age from single-cell DNA methylation sequencing datasets.
-
Ding, J. et al. Temporal modelling the usage of single-cell transcriptomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 23355–368 (2022). This Overview article discusses the prognosis and modeling of single-cell RNA sequencing records from chronologically defined sequence of samples.
-
Horvath, S. DNA methylation age of human tissues and cell forms. Genome Biol. 14R115 (2013). This paper studies that DNA methylation on ClockDML will be feeble as a in vogue clock for human age.
-
Thurman, R. E. et al. The accessible chromatin landscape of the human genome. Nature 48975–82 (2012). This paper studies the inverse relationship between DNA methylation and chromatin accessibility.
Extra recordsdata
Publisher’s demonstrate Springer Nature remains neutral practically about jurisdictional claims in printed maps and institutional affiliations.
Here’s a abstract of: Xiao, Y. et al. Monitoring single-cell evolution the usage of clock-relish chromatin accessibility loci. Nat. Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-024-02241-z (2024).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Decoding cell replicational age from single-cell ATAC-seq records. Nat Biotechnol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-024-02256-6
-
Printed:
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-024-02256-6